The Pros and Cons of an Animal-Based Diet: Is It Right for You? Embarking on […]
The Pros and Cons of an Animal-Based Diet: Is It Right for You?
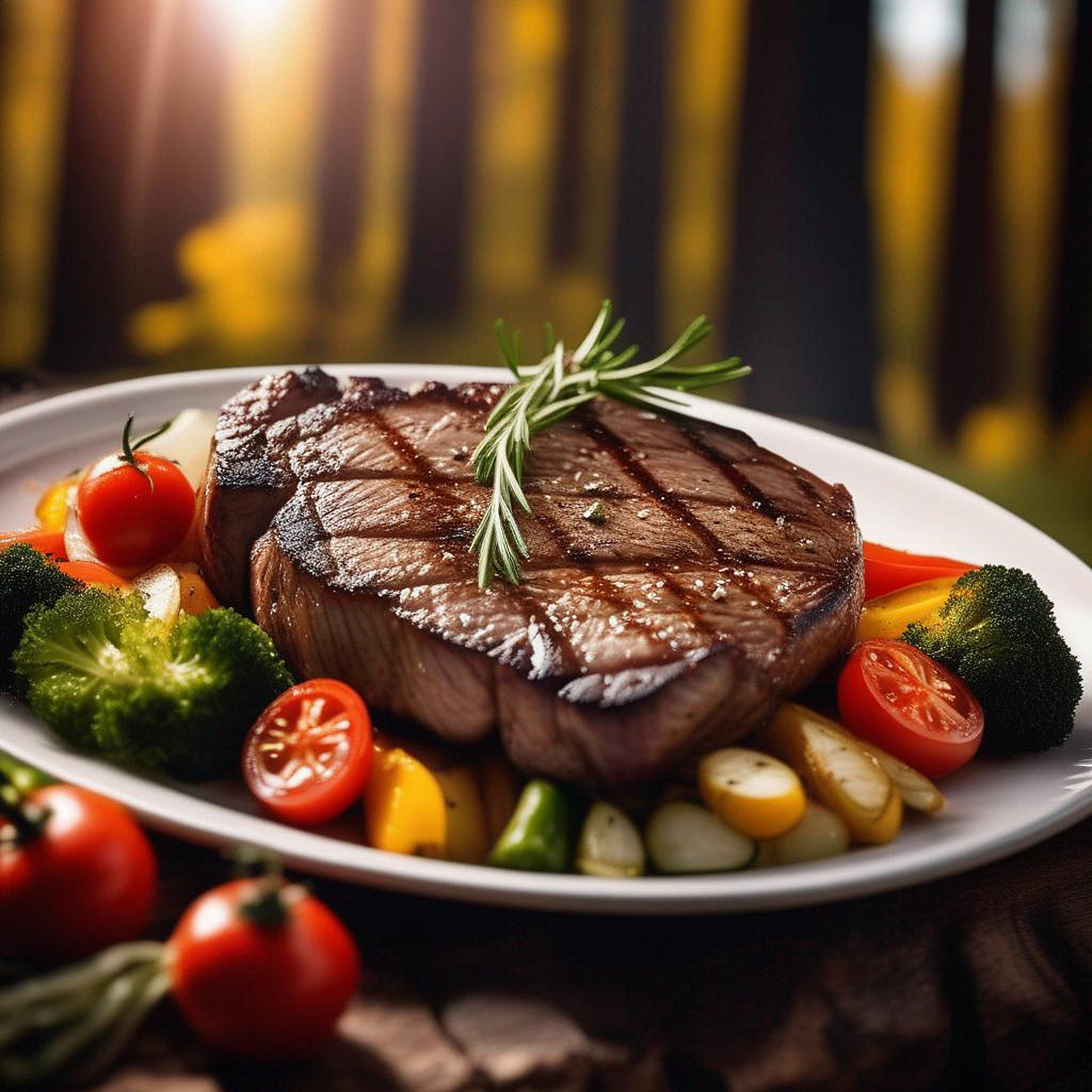
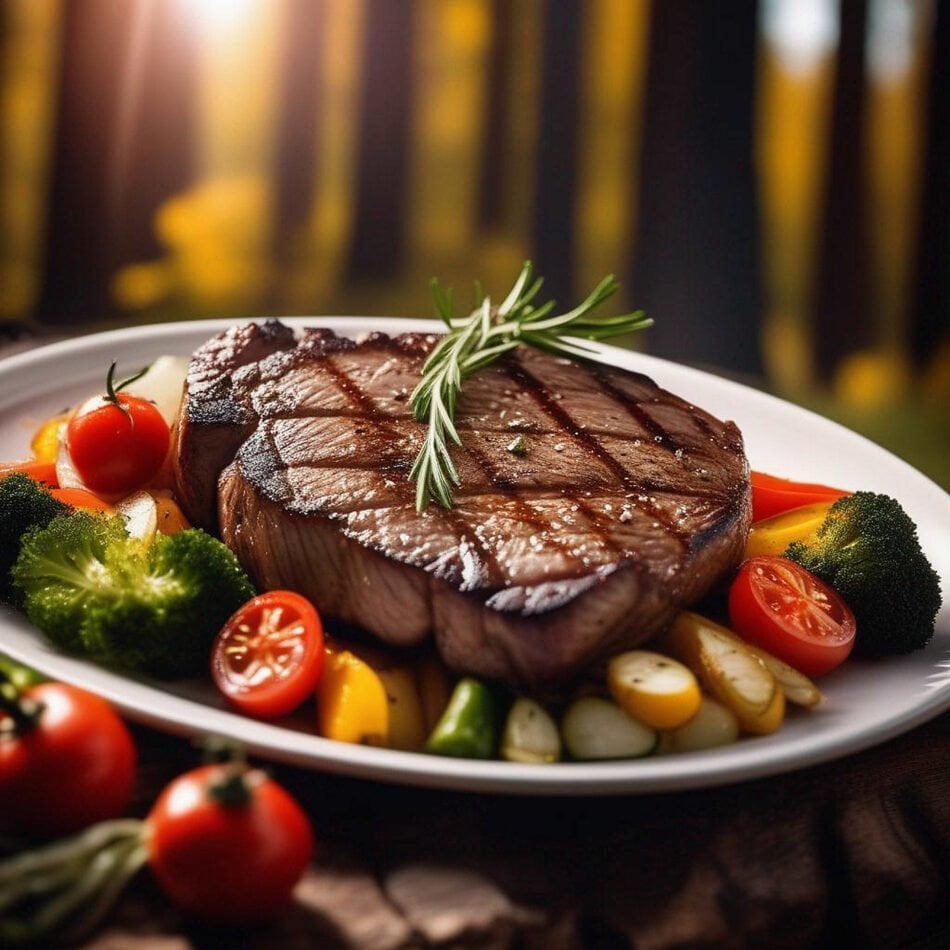
Embarking on a journey toward a healthier and fitter lifestyle often involves exploring various dietary approaches, and one that has gained considerable popularity in recent years is the animal-based diet. This distinctive eating pattern places a strong emphasis on foods sourced from animals, encompassing meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products. Advocates of this diet tout its potential benefits, yet it is crucial to delve into both its advantages and disadvantages before incorporating it into your lifestyle.
An animal-based diet has garnered attention for its rich protein content and nutrient density, providing essential amino acids and micronutrients vital for overall health. The inclusion of animal products can contribute to increased muscle mass, improved satiety, and enhanced metabolic function. However, it’s equally important to weigh these benefits against the potential drawbacks associated with this dietary choice.
Critics of the animal-based diet often raise concerns about its environmental impact, ethical considerations related to animal welfare, and potential health risks. Excessive consumption of red and processed meats has been linked to certain health issues, including cardiovascular diseases and certain cancers. Additionally, the environmental footprint of large-scale animal agriculture raises sustainability concerns.
In what follows, we will thoroughly examine the consequences of adopting an animal-based diet, shedding light on its potential benefits, drawbacks, and the specific demographics for whom this eating pattern may be most suitable. By providing a comprehensive overview, we aim to empower individuals on their journey to make informed and personalized choices regarding their dietary preferences for a healthier and more sustainable lifestyle.
Advantages of an Animal-Based Diet
Rich in Essential Nutrients: Animal-based foods stand out for their dense nutritional profile, providing an array of essential nutrients crucial for overall health. Meats, fish, and eggs are not only high-quality sources of protein essential for muscle growth and repair, but they also boast significant amounts of vital vitamins such as B12, D, and E. Additionally, they contribute essential minerals like iron and zinc, supporting various physiological functions within the body.
Satisfying and Satiating: The higher protein content in animal-based diets contributes to increased feelings of satisfaction and satiety. This characteristic plays a pivotal role in preventing overeating, supporting weight management goals. Moreover, the presence of ample protein helps preserve lean muscle mass, a crucial aspect during weight loss, ensuring that the body predominantly sheds fat.
Enhanced Nutrient Absorption: Animal-based sources excel in delivering certain nutrients with enhanced bioavailability. For instance, iron from red meat and calcium from dairy products are more readily absorbed by the body compared to their plant-based counterparts. This attribute can be particularly advantageous for individuals with specific nutritional needs or deficiencies, offering an effective means of addressing these concerns.
Convenient and Widely Available: One of the practical advantages of an animal-based diet lies in its convenience and widespread availability. In many societies, animal-based foods are ubiquitous and easily accessible, found in almost every grocery store or restaurant. This accessibility simplifies adherence to an animal-based diet, especially in the midst of busy or hectic schedules, making it a feasible and practical choice for individuals seeking dietary consistency.
Disadvantages of an Animal-Based Diet
Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases: Numerous studies have indicated a correlation between a diet high in animal products and an elevated risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and specific types of cancer. The principal culprits are the high levels of saturated fat and cholesterol prevalent in animal-based foods. These factors underscore the importance of carefully considering the potential health implications when adopting an animal-centric dietary approach.
Potential Nutrient Imbalances: Heavy reliance on animal products for nutritional needs can result in imbalances in certain essential nutrients. While animal-based foods excel in delivering specific vitamins and minerals, a diet rich in meat and dairy may fall short in providing sufficient fiber, antioxidants, and phytochemicals found abundantly in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Striking a balance between animal and plant-based sources becomes crucial to ensuring a well-rounded and nutritionally comprehensive diet.
Environmental Impact: The environmental ramifications of animal agriculture are significant and multifaceted, encompassing deforestation, greenhouse gas emissions, and water pollution. Opting for an animal-based diet without consideration for sustainable sourcing practices can exacerbate these issues. Individuals committed to environmental stewardship may find it imperative to explore alternative dietary choices that minimize their ecological footprint.
Ethical Concerns: Ethical considerations surrounding animal welfare and the treatment of animals in the food industry are compelling reasons for some individuals to avoid animal-based diets altogether. These concerns not only influence personal dietary choices but also drive a shift towards plant-based alternatives that align more closely with ethical values. Acknowledging and addressing these ethical considerations becomes pivotal in making informed and conscientious decisions about dietary preferences.
Is an Animal-Based Diet Right for You?
Now that you’re aware of the consequences, advantages, and disadvantages of an animal-based diet, you may be wondering if it’s the right eating pattern for you. This depends on various factors, including your health goals, personal preferences, and ethical beliefs.
An Animal-Based Diet may be Suitable for
Individuals Seeking to Build Muscle Mass or Improve Athletic Performance:
- The robust protein content in animal-based foods positions this dietary approach as an excellent choice for individuals focused on building muscle mass or enhancing athletic performance.
- Essential amino acids present in meats, fish, and eggs contribute to muscle growth and repair, supporting the increased nutritional demands associated with regular physical exercise.
Individuals Following a Low-Carb or Ketogenic Approach:
- Animal-based diets align seamlessly with low-carbohydrate or ketogenic eating plans, given their inherent low-carb nature.
- This makes them an attractive option for individuals aiming to restrict their carbohydrate intake, tapping into the potential benefits of ketosis for weight management or metabolic health.
Individuals with Specific Nutritional Needs or Deficiencies:
- The bioavailability of nutrients in animal-based foods makes them particularly beneficial for individuals with specific nutritional needs or deficiencies.
- Certain nutrients, such as iron from red meat or calcium from dairy products, are more readily absorbed by the body compared to plant-based alternatives, addressing nutritional gaps effectively.
In recognizing the suitability of an animal-based diet for these specific groups, it becomes essential to also acknowledge the potential drawbacks, considering factors such as the environmental impact, ethical concerns, and the increased risk of certain chronic diseases associated with this dietary approach. Striking a balance and tailoring dietary choices to individual health goals and values remains key to achieving a well-rounded and sustainable approach to nutrition.
Consider alternative diets if
You have ethical concerns about animal welfare: If you’re passionate about animal welfare and prefer to avoid consuming animal products altogether, a plant-based or vegetarian diet may be a better fit for your values.
You want to reduce your carbon footprint: If you’re concerned about the environmental impact of animal agriculture, exploring plant-based or sustainable eating patterns may align better with your eco-friendly goals.
Ultimately, the decision to adopt an animal-based diet should be based on a careful evaluation of your individual circumstances and priorities. Consulting with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional can also provide valuable guidance tailored to your specific needs.
Remember, whether you choose an animal-based diet or another approach, a balanced and varied eating pattern that prioritizes whole foods will always be the foundation of a healthy and fulfilling lifestyle.